TYPE OF ITR
ITR Forms
ITR forms i.e. the return filing forms have been prescribed differently based on the class of taxpayers and the source of income. See below for further clarity
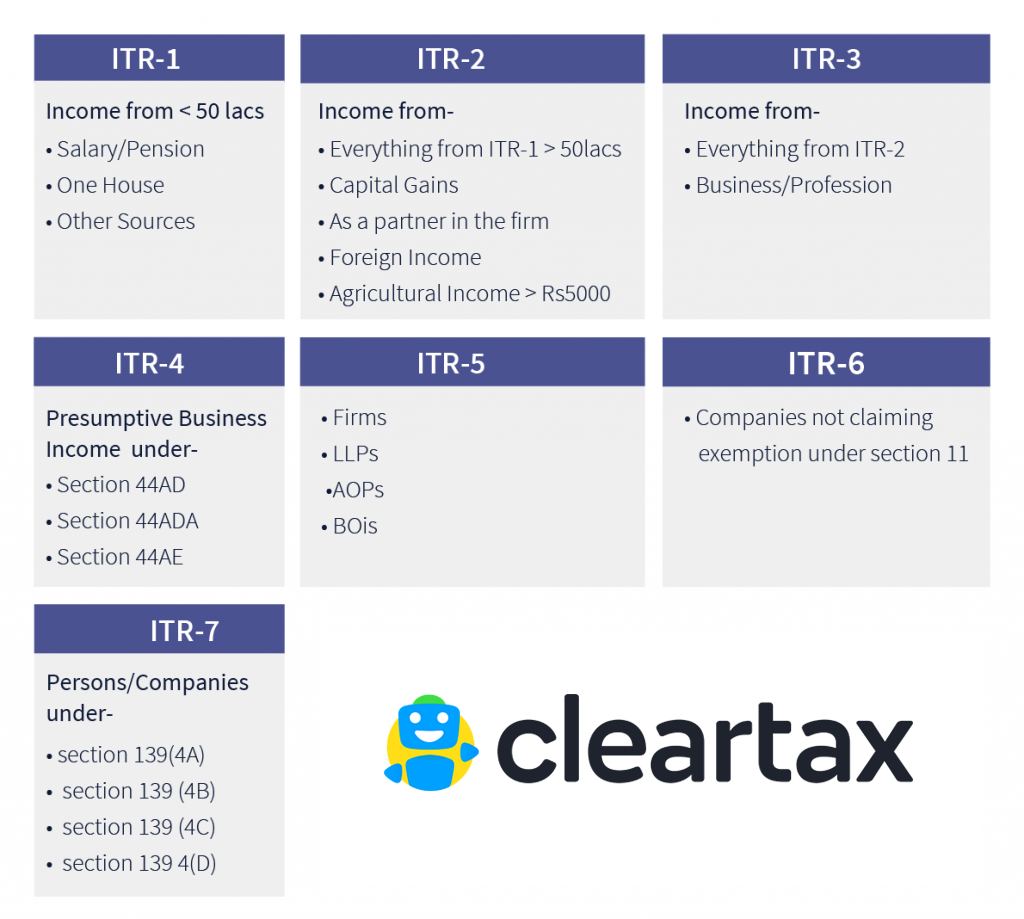 The different forms of ITR are given in detail below, and based on the income level of the individual; one should decide which is the appropriate form to file ITR in India.
The different forms of ITR are given in detail below, and based on the income level of the individual; one should decide which is the appropriate form to file ITR in India.

The different forms of ITR are given in detail below, and based on the income level of the individual; one should decide which is the appropriate form to file ITR in India.
ITR form-1:
For salaried individuals. This form is also called SAHAJ.
Should be used by whose final income for the assessment year is
- Income from salary and pensions.
- Income from single house ownership.
- Income from other sources excluding lotteries and racehorses.
Not applicable to use this form:
- If you are having assets outside the country.
- If there is income from the equity market.
- Agricultural Income – more than 5000.
For salaried individuals. This form is also called SAHAJ.
Should be used by whose final income for the assessment year is
- Income from salary and pensions.
- Income from single house ownership.
- Income from other sources excluding lotteries and racehorses.
Not applicable to use this form:
- If you are having assets outside the country.
- If there is income from the equity market.
- Agricultural Income – more than 5000.
ITR 2 :
Should be used by whose final income for the assessment year is
- Only Salary Incomes
- Income from House Properties
- Income from equity markets
- Income from other sources
Not applicable to use this form:
- If there is income from business or profession
- If you receive any remuneration as a partner in partnership firm / LLP
The main difference between the two above mentioned forms is ITR 1 is not applicable to the individual owning more than a single house, while ITR 2 is applicable.
Should be used by whose final income for the assessment year is
- Only Salary Incomes
- Income from House Properties
- Income from equity markets
- Income from other sources
Not applicable to use this form:
- If there is income from business or profession
- If you receive any remuneration as a partner in partnership firm / LLP
The main difference between the two above mentioned forms is ITR 1 is not applicable to the individual owning more than a single house, while ITR 2 is applicable.
ITR 3:
Should be used by an individual or a HUF who is
- Partner in a Partnership firm or LLP
- Income from business/profession
- Income from firms in the name of anything (bonuses, commission, remuneration, etc.,)
Not applicable to use this form:
- If there is income from business/profession from sole proprietorship.
Should be used by an individual or a HUF who is
- Partner in a Partnership firm or LLP
- Income from business/profession
- Income from firms in the name of anything (bonuses, commission, remuneration, etc.,)
Not applicable to use this form:
- If there is income from business/profession from sole proprietorship.
ITR 4S:
This is also called SUGAM. Should be used by HUF and small business having
- Presumptive Business Income
- Salary / Pension
- One house property
- Income from other sources.
Not applicable to use this form:
- If there is income from capital gains.
- Agricultural Income – more than 5000.
- If there are any speculative incomes
- Winning from lotteries/race horses
- Equity gains
This is also called SUGAM. Should be used by HUF and small business having
- Presumptive Business Income
- Salary / Pension
- One house property
- Income from other sources.
Not applicable to use this form:
- If there is income from capital gains.
- Agricultural Income – more than 5000.
- If there are any speculative incomes
- Winning from lotteries/race horses
- Equity gains
ITR 4:
Should be used by individuals or Hindu Undivided families who are into proprietorship
Should be used by individuals or Hindu Undivided families who are into proprietorship
ITR 5:
Should be used by firms, LLP’s, Association of Persons and Body of Individuals, Artificial Judicial Persons, Cooperative Societies or any local authorities.
Should be used by firms, LLP’s, Association of Persons and Body of Individuals, Artificial Judicial Persons, Cooperative Societies or any local authorities.
ITR 6:
Should be used by companies other than the one who claims exemption under section 11.
Should be used by companies other than the one who claims exemption under section 11.
ITR 7:
Should be used by the individuals and companies, who want to file returns under Section- 139 (4A), Section- 139(4B), Section- 139(4C), Section- 139(4D).
How to Prepare your ITR:
After equipped with adequate information, it is time to decide what form will be appropriate for you and start the process of E-Filing.
Should be used by the individuals and companies, who want to file returns under Section- 139 (4A), Section- 139(4B), Section- 139(4C), Section- 139(4D).
How to Prepare your ITR:
After equipped with adequate information, it is time to decide what form will be appropriate for you and start the process of E-Filing.
"Types of Income" under Income Tax Act. 1956.
Broadly income can be divided into two categories :
- Indian Income
- Foreign Income
A. Indian Income
Indian income is called by various words and names. These are
(1) Income earned in India.
(2) Income accrues and arises in India.
(3) Income received or deemed to be received in India.
(4) Income payable in India. Income may have been earned in a foreign country but it is payable in India.
(5) Income earned (or accrues) in India but is is received or payable outside India.
B. Foreign Income
Following types of incomes are called foreign incomes
(1) Income earned (or accrues) outside India and also received outside India.
(2) Any income which is not earned or accrues or arises in India.
Broadly income can be divided into two categories :
A. Indian Income
Indian income is called by various words and names. These are
(1) Income earned in India.
(2) Income accrues and arises in India. (3) Income received or deemed to be received in India. (4) Income payable in India. Income may have been earned in a foreign country but it is payable in India. (5) Income earned (or accrues) in India but is is received or payable outside India.
B. Foreign Income
Following types of incomes are called foreign incomes
(1) Income earned (or accrues) outside India and also received outside India.
(2) Any income which is not earned or accrues or arises in India. |

No comments: